Categories
New Blog
PRD: A Way Enhancing Efficient Communication with OEM Manufacturers
The journey from the initial concept to the
mass production of an outstanding product often involves extensive
communication. As market competition intensifies, many brand companies opt to
separate business from manufacturing, increasingly choosing to work with OEM
manufacturing service providers. In many cases, brand companies delegate the
development and improvement of new products to manufacturing service providers.
Consequently, complex communication occurs within company departments and
extends to communication between the company and manufacturing service
suppliers. In various industries, such as small household appliances such as wall
mounted air purifiers and consumer electronics such as Bluetooth headsets,
it is common for inefficient communication to extend product development cycles
or lead to products that do not meet expectations. To improve communication
efficiency and optimize development work, effectively utilizing a Product
Requirements Document (PRD) is an excellent approach.
What is a Product Requirements Document?
A Product Requirements Document,
abbreviated as PRD, is a document used in the product development process to
define and describe the features, characteristics, performance, and other
relevant requirements of a product. It serves as a crucial communication tool
to ensure that the team shares a common understanding of the product's design
and development.
The Role of a Product Requirements
Document
PRD plays a vital role in the product
development and production process, typically serving the following purposes:
Clarifying Product Goals: The PRD can articulate the goals and vision of the product. By
detailing requirements in terms of functionality, performance, and features,
the team can collectively understand the ultimate goals and expected outcomes
of it.
Communication and Collaboration: Development teams, design teams, testing teams, production teams,
etc., can better understand the project scope through the PRD, facilitating
collaborative efforts to drive project progress.
Development Planning: The PRD contains the product's features and priorities, aiding in
the formulation of a development plan. The development team can set
stage-specific goals and schedule corresponding work based on the information
in the PRD.
Feasibility Assessment: The PRD includes various requirements for the product,
encompassing technical, resource, and time considerations. This helps the team
determine the feasibility of the project in its early stages.
Change Management: While the PRD establishes the basic framework of the product early
in the project, changes in requirements may occur during the project's course.
The PRD helps manage and track these changes to ensure the team can make timely
adjustments. In the context of outsourcing product development to OEM
manufacturing service providers, the role of PRD in helping to improve
communication efficiency will become more evident.
Product Acceptance: After the completion of product development, the PRD serves as a
benchmark for comparing requirements against the delivered results, ensuring
the product meets expectations.
Risk Reduction: By thoroughly describing requirements in the document, the team
can identify potential issues early on and take appropriate measures to
mitigate risks.
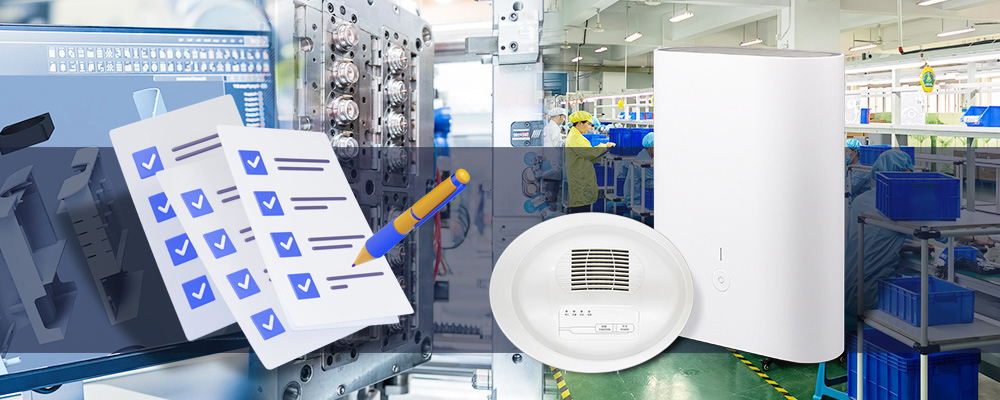
How to Achieve these Functions through a
Product Requirements Document
To achieve the aforementioned functions
through a Product Requirements Document, the document should possess a series of
key elements and features. Here are some recommendations to help you create a
PRD with practical impact:
Clear and Concise Product Vision: Clearly state the product's vision and goals at the beginning of
the document. Ensure that all team members understand the general direction and
value proposition.
Detailed Feature Descriptions: List each function and feature of the product, including user
interface, operation process, work logic, etc. Ensure each feature has a clear
description, avoiding vague or ambiguous expressions.
Ser Stories and Use Cases: Use user stories and use cases to describe how users will interact
with the product in different scenarios. This helps the development team better
understand user requirements and, in turn, meet user expectations.
Performance and Quality Requirements: Define performance indicators and quality standards for the
product. Clearly state the expected performance in various aspects, such as
functionality, safety, and maintainability.
Priorities and Timetable: Provide priorities for different features to help the team focus
on critical tasks within the limited time. Additionally, offer a rough
timetable to inform the team when each phase of work needs completion.
Technical Requirements and Limitations: Determine the technical requirements of the product, including
hardware and software specifications. Also, clarify potential technical
limitations early in the project for consideration and resolution.
Change Management Mechanism: Establish a clear change management mechanism to handle potential
requirement changes during the project cycle. This may include evaluating the
impact of changes and an approval process.
Testing Plan:
Describe the product's testing plan, covering unit testing, integration
testing, and user acceptance testing. Ensure the team conducts comprehensive
testing before product delivery.
Risk Analysis and Mitigation Measures: Conduct a risk analysis for potential project risks and provide
corresponding mitigation measures. This helps the team address potential issues
more effectively during the project.
Team Roles and Responsibilities: Clearly define the roles and responsibilities of each team member,
ensuring everyone understands their contributions and responsibilities
throughout the project.
Take an example:
Let's consider developing a private
label air purifier as an example. In the PRD, articulate the product vision
at the beginning, such as improving indoor air quality and enhancing users'
quality of life. Specific functionalities may include efficient filtration of
PM2.5 particles, smart air quality monitoring, and low-noise operation.
Regarding technical requirements, specify the needs of using high-efficiency
HEPA filters, smart sensors, and other advanced technologies. Provide a clear
testing plan that covers performance testing and user experience testing to
ensure the product meets high-quality standards. Emphasize the use of
sustainable materials to promote environmental friendliness.
To enhance efficiency in development and
production, the PRD should outline a timetable, dividing the development
stages, such as prototype design, prototype manufacturing, and mass production.
This helps manufacturing service providers better plan resources. Define a
clear change management process to promptly handle any requirement changes,
ensuring information synchronization. Through user stories and use cases,
vividly describe the experiences the purchaser expects users to have in
different usage scenarios, providing manufacturing partners with a more
intuitive understanding of the product. Regular updates and communication
ensure all stakeholders maintain a consistent understanding of the overall
project direction. Through such a comprehensive PRD, brand purchasers and OEM
air purifier manufacturing service suppliers can collaborate more
efficiently to achieve common goals.
In conclusion, creating an excellent
product is a challenging process. Effectively utilizing a PRD can improve
communication efficiency within internal teams or between a company and
manufacturing service providers. This may expedite the launch of your ideal
product, gaining a competitive edge.

Copyright © 2012-2026 Xiamen Atyou Health Technology Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.