Categories
New Blog
Using Prototypes Effectively to Assist Brands and Manufacturers in Developing Ideal Exclusive Products
In the process of developing new products,
from designing requirement documents to final mass production, there are often
critical decision-making moments. Questions such as whether the new product has
reached development goals, whether there's room for further improvement in user
experience, and whether the product is mature enough to start production are
all critical issues that require solid evidence for decision-making. However,
making accurate assessments based solely on design documents is challenging.
Instead of relying on blueprints, it's more reliable to obtain data through
firsthand observation. Therefore, prototype samples become an indispensable key
stage in the development and mass production of new products. Whether it's
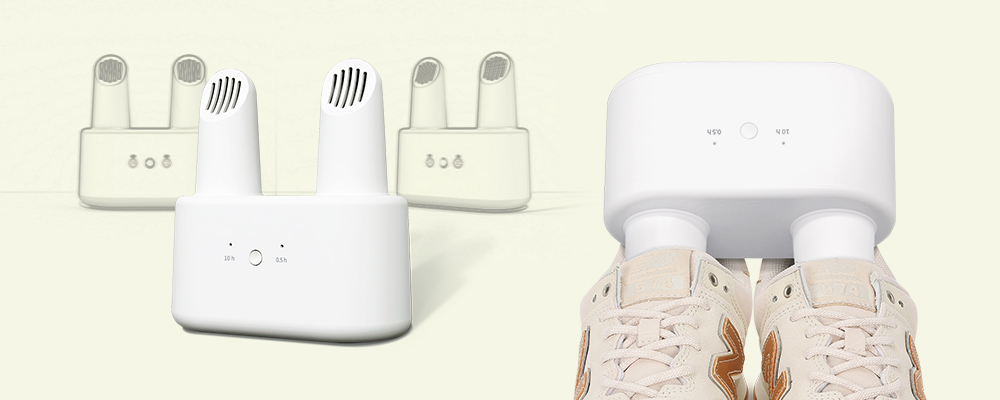
small products like Bluetooth earphones, UV baby bottle sterilizers,
shoe dryers, or large equipment like air purifiers, ovens, and refrigerators,
prototypes can help us more accurately optimize the development of new products
and make wise decisions at critical moments.
What is a Prototype?
A prototype is a physical model or sample
created during the product design process, aimed at demonstrating, validating,
and testing the design concepts, functional performance, appearance features,
and manufacturing feasibility of the product. It's an early-stage physical
model typically used to check and improve product design to ensure the final
product can meet specific requirements and standards. Prototypes can be created
at various stages of the product development cycle, with the aim of providing a
visual and tangible object to help design teams and stakeholders better
understand, evaluate, and improve product design.
The Role of Prototypes
Prototypes play a crucial role in the product
development and serve various purposes. Here are the main functions of
prototypes:
Validating Design Concepts: Prototypes are used to validate the product design concepts and
ideas. Through physical models, design teams can visually inspect and feel the
product's appearance, shape, and overall design to ensure it meets the desired
goals.
Testing Functional Performance: Prototypes allow for testing and validating the core functionalities
of a product. This helps identify and address any technical issues that may
exist during the design phase, ensuring the product operates as expected in
real-world use.
User Experience Testing: Through user experience prototypes, design teams can assess how
users interact with the product, examining its usability and user satisfaction.
This helps optimize the product's user interface and user experience.
Identifying and Solving Problems: Creating prototypes helps identify problems in the design or
manufacturing process. By testing and evaluating prototypes, teams can identify
and address issues that may cause product failure or failure to meet
requirements.
Reducing Development Risks: Building prototypes helps reduce risks during the product
development phase. Early identification and resolution of issues can prevent
costly changes and repairs later in production.
Improving Design Quality: Through iterative testing and modification of prototypes, design
teams can gradually improve the product design quality. This helps ensure the
final product is more competitive in the market.
Communication and Collaboration: Prototypes provide a common physical model for design teams,
engineering teams, and other stakeholders, facilitating more effective
communication and collaboration. This helps ensure that each team member's
expectations and requirements for the product are consistent.
Market Testing: Trial production prototypes can be used for market testing to
evaluate the product's performance in market environments. This helps develop
more accurate market strategies and promotion plans.
Overall, prototypes play a crucial role in
the product development process, helping to improve product quality, reduce
risks, and ensure successful product launches.
One Example:
Let's take the development of a portable
shoe dryer as an example. First, the design team may produce one or several
concept validation prototypes. These prototypes may include appearance
prototypes that materialize the drawings and functional prototypes that add
core product functions. They will be used to verify the basic design concepts
of the product, including the appearance design, product size and the
feasibility of the shoe drying function. Through these physical objects, the
design team can visually inspect and feel the appearance, size, and operation
of the product design, ensuring that it meets the design requirements and user
expectations. Feedback and test results will help iterate and improve the
design, ensuring the product meets market demand.
Next, engineering validation prototypes
will be manufactured to test the product's engineering performance. These
prototypes may include more details, such as heating elements and power
management systems. Through them, the team can assess the technical feasibility
and check for potential engineering challenges such as performance issues and
power supply problems. This helps address potential issues and ensure the
stable operation of the product during manufacturing.
Finally, when entering the production
stage, the production team or OEM shoe dryer manufacturers will conduct
small-scale trial production to produce some trial production prototypes
according to the actual production process. This is done to verify the
rationality of mass production processes and optimize production costs. At the
same time, these trial production prototypes can also be provided to the
marketing team for early marketing and market testing. The entire prototype
development process will iterate through multiple stages to ultimately achieve
a portable shoe dryer that is reliable, visually appealing, and meets customer
economic needs.

Copyright © 2012-2025 Xiamen Atyou Health Technology Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.